Chemical formula vanadium iii selenide invites us to embark on a journey of scientific discovery, where we delve into the intricate world of this captivating compound. Its unique properties and diverse applications make it a subject of great interest, promising to unravel a wealth of knowledge and practical insights.
This comprehensive exploration of vanadium iii selenide will illuminate its chemical structure, physical and chemical properties, industrial applications, production methods, and safety considerations. Prepare to be captivated as we unravel the secrets of this remarkable material, unlocking its potential for technological advancements and scientific breakthroughs.
Chemical Formula Vanadium III Selenide

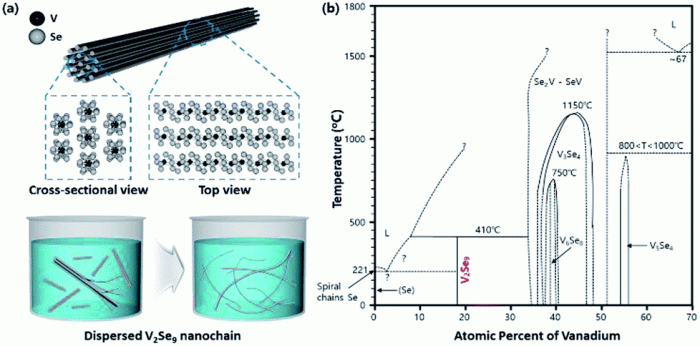
Vanadium iii selenide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula VSe 3. It is a dark, metallic-looking solid that is insoluble in water. VSe 3is a semiconductor with a band gap of 1.3 eV.
Chemical Structure
VSe 3has a layered structure, with each layer consisting of a hexagonal lattice of vanadium atoms sandwiched between two layers of selenium atoms. The vanadium atoms are in the +3 oxidation state, and the selenium atoms are in the
2 oxidation state.
Properties: Chemical Formula Vanadium Iii Selenide
Physical Properties
Vanadium iii selenide is a dark, metallic-looking solid with a melting point of 685 °C and a boiling point of 1400 °C. It is insoluble in water.
Chemical Properties
VSe 3is a semiconductor with a band gap of 1.3 eV. It is a relatively stable compound, but it can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents. VSe 3is also a good conductor of electricity.
Applications
Vanadium iii selenide is used in a variety of applications, including:
Batteries
VSe 3is used as a cathode material in lithium-ion batteries. It has a high theoretical capacity and a good cycle life.
Semiconductors
VSe 3is used as a semiconductor in a variety of electronic devices, including solar cells, photodiodes, and transistors.
Catalysts
VSe 3is used as a catalyst in a variety of chemical reactions, including the hydrogenation of alkenes and the oxidation of alcohols.
Production
Vanadium iii selenide can be produced by a variety of methods, including:
Direct Synthesis
VSe 3can be synthesized by directly reacting vanadium and selenium powders at high temperatures.
Chemical Vapor Deposition
VSe 3can be synthesized by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In this process, vanadium tetrachloride (VCl 4) and hydrogen selenide (H 2Se) are reacted in a heated chamber.
Electrochemical Deposition, Chemical formula vanadium iii selenide
VSe 3can be synthesized by electrochemical deposition. In this process, a vanadium electrode is placed in a solution of selenium dioxide ( 2). When an electric current is passed through the solution, VSe 3is deposited on the electrode.
Safety
Vanadium iii selenide is a toxic compound. It can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. VSe 3can also be harmful if ingested or inhaled. When working with VSe 3, it is important to wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves, a lab coat, and a respirator.
Clarifying Questions
What is the chemical formula for vanadium iii selenide?
V3Se4
What is the appearance of vanadium iii selenide?
Dark gray or black powder
What is the melting point of vanadium iii selenide?
1670°C
What is the boiling point of vanadium iii selenide?
1900°C
Is vanadium iii selenide toxic?
Yes, it can be harmful if inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin.