Relationship attachment model john van epp – John Van Epp’s Relationship Attachment Model (RAM) provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the dynamics of human relationships. Rooted in attachment theory, RAM offers a nuanced perspective on the ways in which early experiences shape our capacity for intimacy, communication, and conflict resolution.
This model has gained significant recognition for its ability to explain the complexities of human attachment and its impact on relationship outcomes. By examining the interplay between attachment styles, patterns, and dynamics, RAM provides valuable insights for therapists, researchers, and individuals seeking to enhance their relationships.
Attachment Theory and the Relationship Attachment Model
Attachment theory, proposed by John Bowlby, posits that early childhood experiences with primary caregivers shape an individual’s capacity for forming close relationships. The Relationship Attachment Model (RAM), developed by John Van Epp, expands on attachment theory by focusing on the dynamic interplay between attachment styles, patterns, and dynamics within romantic relationships.
RAM distinguishes itself from other attachment models by emphasizing the influence of relationship context on attachment experiences. It recognizes that attachment styles can change over time and across relationships, influenced by the specific interactions and experiences within each relationship.
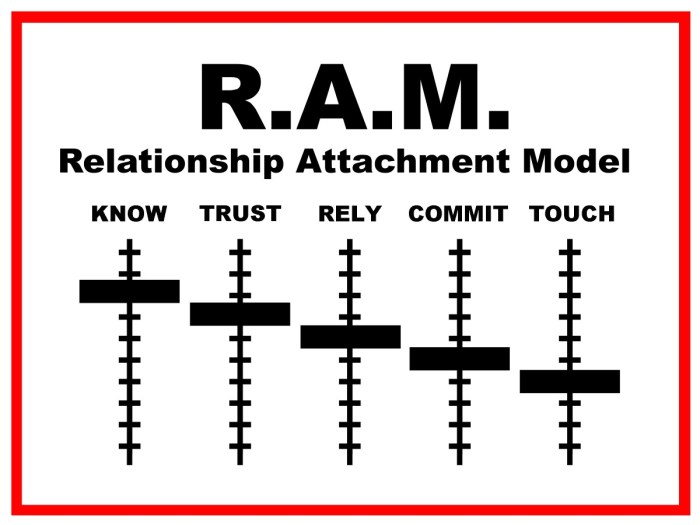
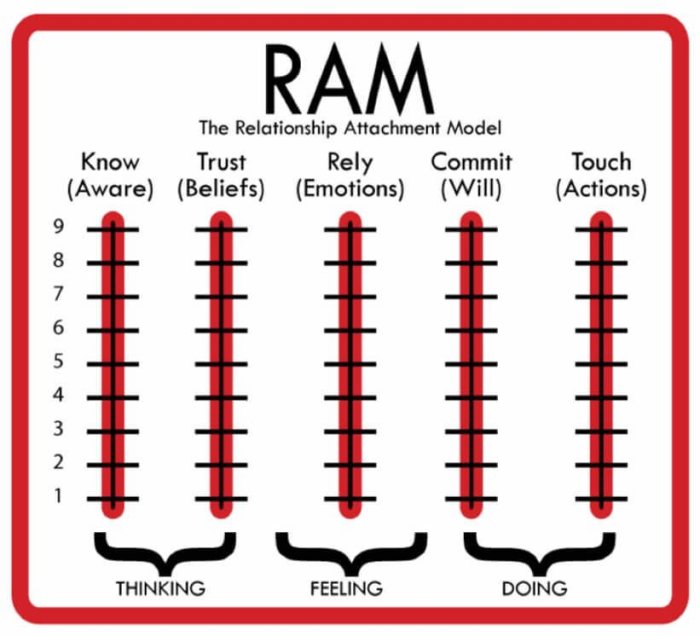
Key Components of the Relationship Attachment Model: Relationship Attachment Model John Van Epp
Attachment Style
RAM identifies four primary attachment styles: Secure, Avoidant, Anxious-Ambivalent, and Disorganized. Each style is characterized by specific patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in relationships.
Attachment Patterns
Attachment patterns refer to the ways in which individuals interact with their partners based on their attachment style. These patterns emerge from the reciprocal interactions between partners and shape the overall dynamics of the relationship.
Attachment Dynamics
Attachment dynamics encompass the ongoing processes and interactions that occur within a relationship, influenced by the attachment styles and patterns of both partners. These dynamics can either enhance or hinder relationship satisfaction and stability.
Attachment Styles and Relationship Outcomes
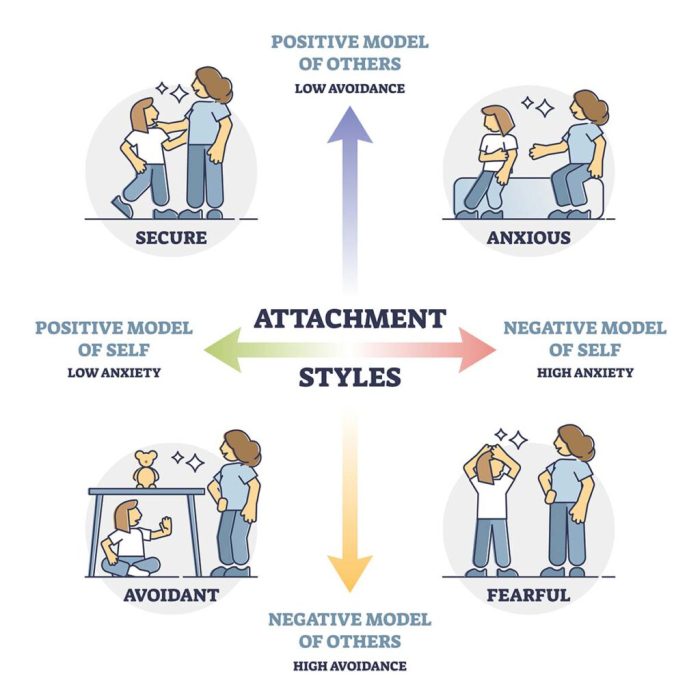
Secure Attachment
- Characterized by trust, comfort, and openness in relationships.
- Individuals with secure attachment tend to have higher relationship satisfaction and lower levels of anxiety and avoidance.
Avoidant Attachment
- Individuals with avoidant attachment tend to be emotionally distant and independent.
- They may have difficulty forming close relationships and may suppress their need for intimacy.
Anxious-Ambivalent Attachment
- Characterized by intense desire for closeness and fear of abandonment.
- Individuals with anxious-ambivalent attachment may exhibit clingy or demanding behaviors in relationships.
Disorganized Attachment
- A combination of secure and insecure attachment styles, characterized by inconsistent and unpredictable behavior.
- Individuals with disorganized attachment may have difficulty regulating their emotions and forming stable relationships.
Attachment Patterns and Relationship Development
Attachment patterns develop over time and across relationships. Early attachment experiences can influence the formation of attachment patterns, but they can also be shaped by subsequent relationships and life experiences.
Attachment patterns impact relationship stability, intimacy, and trust. Secure attachment patterns tend to promote healthy and fulfilling relationships, while insecure attachment patterns can lead to relationship difficulties and distress.
Attachment Dynamics and Relationship Therapy
Attachment Dynamics in Relationships, Relationship attachment model john van epp
- Attachment anxiety: One partner’s anxious attachment style can trigger anxiety and avoidance in the other partner.
- Attachment avoidance: One partner’s avoidant attachment style can lead to withdrawal and disengagement in the other partner.
- Attachment conflict: Differences in attachment styles can lead to conflicts and misunderstandings.
Attachment Dynamics in Therapy
Therapists can help couples understand their attachment styles and patterns and develop strategies to address attachment dynamics that are contributing to relationship distress.
- Psychoeducation: Providing information about attachment theory and its implications for relationships.
- Communication training: Improving communication skills to facilitate open and honest discussions about attachment needs.
- Emotion regulation techniques: Teaching coping mechanisms for managing anxiety and avoidance.
Expert Answers
What are the key components of the Relationship Attachment Model?
The key components of RAM are attachment styles, attachment patterns, and attachment dynamics.
How do attachment styles influence relationship outcomes?
Attachment styles can significantly impact relationship satisfaction, communication, and conflict resolution. For instance, individuals with secure attachment styles tend to have more satisfying relationships characterized by trust, open communication, and effective problem-solving.
What is the role of attachment dynamics in shaping relationship outcomes?
Attachment dynamics refer to the ways in which individuals interact with each other based on their attachment styles. These dynamics can contribute to relationship distress and dysfunction if they are characterized by insecurity, avoidance, or ambivalence.