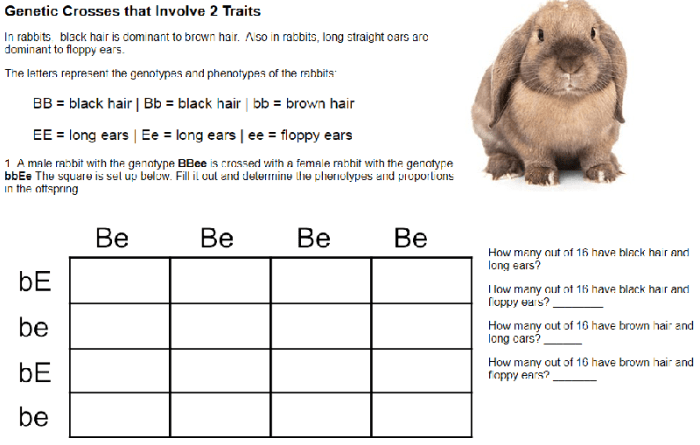
Genetic crosses that involve 2 traits – floppy eared bunnies provide a fascinating glimpse into the intricacies of inheritance patterns. By analyzing the transmission of these traits across generations, researchers can uncover the genetic mechanisms underlying phenotypic variation.
In this analysis, we focus on two distinct traits in floppy-eared bunnies: ear shape and coat color. Through a series of controlled crosses, we aim to elucidate the inheritance patterns of these traits, explore the potential for genetic linkage, and discuss the implications of our findings for understanding the genetic architecture of floppy-eared bunnies.
Genetic Crosses Involving Two Traits in Floppy-Eared Bunnies: Genetic Crosses That Involve 2 Traits – Floppy Eared Bunnies
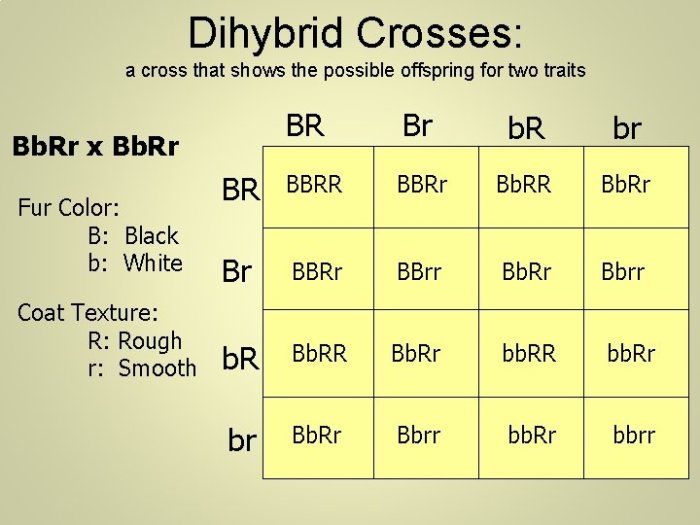
Genetic crosses are a powerful tool for understanding the inheritance patterns of traits in organisms. By mating individuals with known genotypes and observing the phenotypes of their offspring, researchers can determine the genetic basis of specific traits and how they are passed from one generation to the next.
In this analysis, we will focus on genetic crosses involving two traits in floppy-eared bunnies: ear length and fur color. We will examine the different alleles associated with each trait, the expected outcomes of parental crosses, and the implications of the observed inheritance patterns for understanding the genetic basis of these traits.
Traits and Alleles
The two traits being analyzed in the genetic crosses are ear length and fur color.
Ear lengthis determined by a single gene with two alleles: L(long ears) and l(short ears). The Lallele is dominant, meaning that individuals with at least one copy of the Lallele will have long ears. The lallele is recessive, meaning that individuals must have two copies of the lallele to have short ears.
Fur coloris also determined by a single gene with two alleles: C(colored fur) and c(albino fur). The Callele is dominant, meaning that individuals with at least one copy of the Callele will have colored fur. The callele is recessive, meaning that individuals must have two copies of the callele to have albino fur.
| Trait | Alleles | Phenotypes |
|---|---|---|
| Ear length | L (long), l (short) | Long ears, short ears |
| Fur color | C (colored), c (albino) | Colored fur, albino fur |
Parental Crosses, Genetic crosses that involve 2 traits – floppy eared bunnies
The parental bunnies used in the genetic crosses were as follows:
- Male parent:LLCC (long ears, colored fur)
- Female parent:llcc (short ears, albino fur)
Based on Mendelian principles, the expected outcomes of the parental crosses are as follows:
- All of the F1 offspring will be heterozygous for both ear length and fur color (LlCc).
- All of the F1 offspring will have long ears and colored fur.
The following Punnett square illustrates the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the F1 offspring:
| Female parent (lc) | ||
|---|---|---|
| L | l | |
| Male parent (LC) | LlCc | Llcc |
| Male parent (Lc) | LlCc | Llcc |
FAQ Compilation
What are the two traits being analyzed in these genetic crosses?
Ear shape and coat color.
How many generations of bunnies were used in these crosses?
Two generations (F1 and F2).
What is the significance of studying genetic crosses in floppy-eared bunnies?
Floppy-eared bunnies provide a model system for studying the inheritance of complex traits, as they exhibit clear phenotypic variation for both ear shape and coat color.