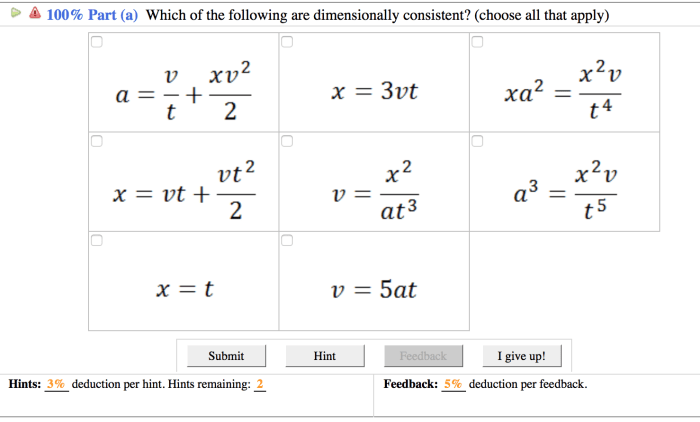
Which of the following equations are dimensionally consistent – In the realm of scientific inquiry, the concept of dimensional consistency emerges as a cornerstone of reliable and accurate calculations. Dimensional consistency ensures that the units of measurement employed in an equation align harmoniously with the physical quantities they represent, a principle that underpins the validity and integrity of scientific investigations.
This article delves into the intricacies of dimensional consistency, exploring its significance, methods of verification, and the consequences of disregarding its principles.
Dimensional consistency serves as a gatekeeper, safeguarding against erroneous conclusions and ensuring the coherence of scientific endeavors. By adhering to its tenets, researchers can confidently navigate the complexities of scientific equations, unraveling the mysteries of the natural world with precision and confidence.
Dimensional Consistency
Dimensional consistency is a fundamental principle in physics and engineering that ensures the validity and reliability of equations. It requires that the dimensions (units) of all terms in an equation match on both sides. This ensures that the physical quantities involved in the equation are compatible and that the equation makes sense physically.The
concept of dimensional consistency stems from the fact that physical quantities have specific dimensions. For example, length is measured in meters (m), mass in kilograms (kg), and time in seconds (s). When these quantities are combined in equations, their dimensions must be consistent to ensure that the equation is meaningful.
Units and Dimensions
Units are the specific standards used to express the magnitude of physical quantities. They provide a common reference point for comparing and quantifying different quantities. For example, the meter is the standard unit of length, the kilogram is the standard unit of mass, and the second is the standard unit of time.Dimensions
are derived from units and represent the fundamental physical properties of quantities. For example, the dimension of length is [L], the dimension of mass is [M], and the dimension of time is [T]. These dimensions can be combined to form the dimensions of more complex quantities, such as velocity ([L]/[T]) and acceleration ([L]/[T]^2).
Checking Dimensional Consistency
To check the dimensional consistency of an equation, follow these steps:
- Identify the physical quantities involved in the equation and their dimensions.
- Multiply each term in the equation by its dimensions.
- Check if the dimensions on both sides of the equation match.
If the dimensions match, the equation is dimensionally consistent. If they do not match, the equation is dimensionally inconsistent and may not be physically meaningful.
Examples of Dimensionally Consistent Equations
The following table shows examples of dimensionally consistent equations from various fields:| Equation | Physical Quantities | Dimensions ||—|—|—|| F = ma | Force (F), mass (m), acceleration (a) | [M][L]/[T]^2 || V = IR | Voltage (V), current (I), resistance (R) | [M][L]^2/[T]^3[A]^2 || E = mc^2 | Energy (E), mass (m), speed of light (c) | [M][L]^2/[T]^2 |
Examples of Dimensionally Inconsistent Equations, Which of the following equations are dimensionally consistent
The following are examples of dimensionally inconsistent equations:
- F = ma + b (where b has dimensions of force)
- V = IR + Q (where Q has dimensions of charge)
- E = mc^3 (where c has dimensions of velocity)
Implications of Dimensional Inconsistency
Using dimensionally inconsistent equations can have serious implications:
- The results of calculations may be incorrect or meaningless.
- Predictions based on the equations may be unreliable.
- The equations may not be able to be used to solve real-world problems.
FAQ Guide: Which Of The Following Equations Are Dimensionally Consistent
What is the significance of dimensional consistency?
Dimensional consistency ensures the alignment between the units of measurement used in an equation and the physical quantities they represent, preventing erroneous conclusions and safeguarding the integrity of scientific calculations.
How can I check the dimensional consistency of an equation?
To verify dimensional consistency, compare the dimensions of each term in the equation. If all terms have the same dimensions, the equation is dimensionally consistent.
What are the consequences of using dimensionally inconsistent equations?
Dimensionally inconsistent equations yield incorrect results and undermine the validity of scientific conclusions. They can lead to erroneous interpretations, wasted resources, and compromised decision-making.