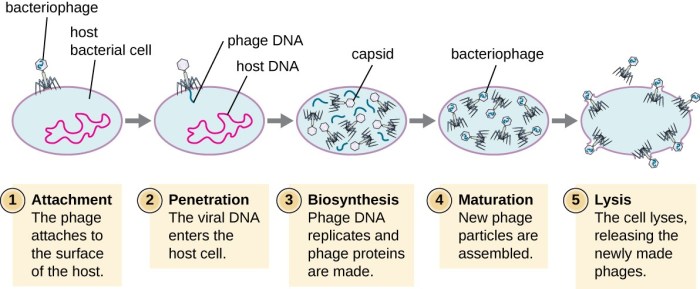
Mature T2 phage particles are released from infected host cells through a complex and precisely orchestrated process. Understanding the mechanisms underlying this release is crucial for advancing our knowledge of viral assembly and release, as well as for developing novel therapeutic strategies.
The assembly of T2 phage particles involves a series of intricate steps, including DNA replication, capsid formation, and tail fiber attachment. The release of mature phage particles is triggered by the action of phage-encoded holin and endolysin proteins, which work together to lyse the host cell membrane and release the phage progeny.
Mature T2 Phage Particle Structure
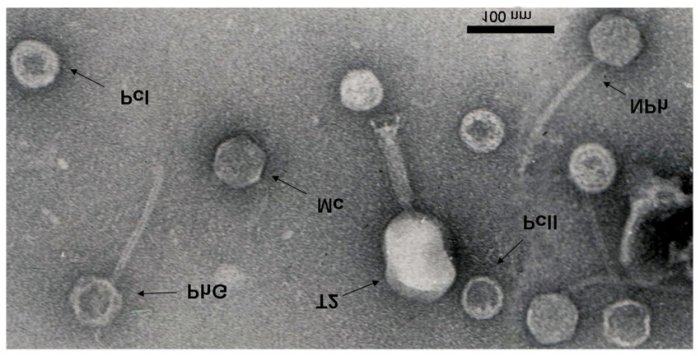
Mature T2 phage particles are highly complex structures composed of various molecular components. The particle consists of a head, tail, and tail fibers. The head is icosahedral in shape and contains the phage’s DNA genome. The tail is a hollow cylinder that extends from the head and is responsible for host cell attachment and DNA injection.
The tail fibers are protein structures that protrude from the end of the tail and play a crucial role in recognizing and binding to specific host cell receptors.
T2 Phage Assembly
T2 phage assembly is a highly orchestrated process that involves the sequential assembly of individual components into a mature particle. The assembly process begins with DNA replication, followed by the formation of the head and tail structures. The phage DNA is packaged into the head by a specialized packaging motor.
The tail and tail fibers are then assembled and attached to the head, completing the mature phage particle.
T2 Phage Release, Mature t2 phage particles are released
Mature T2 phage particles are released from infected host cells through a process known as cell lysis. This process is mediated by two phage-encoded proteins: holin and endolysin. Holin forms pores in the host cell membrane, while endolysin degrades the cell wall.
The combined action of these proteins leads to the lysis of the host cell and the release of mature phage particles.
Applications of T2 Phage Particles
T2 phage particles have been extensively used as a model system for studying viral assembly and release. The well-characterized nature of the phage and its relatively simple structure have made it a valuable tool for understanding the molecular mechanisms of viral replication and infection.In
addition, T2 phage particles have potential applications in phage therapy and biotechnology. Phage therapy involves the use of phages to kill pathogenic bacteria. T2 phage particles have been shown to be effective against a wide range of bacteria, including those that are resistant to antibiotics.
In biotechnology, T2 phage particles have been used as delivery vehicles for gene therapy and as tools for bioengineering.
Helpful Answers: Mature T2 Phage Particles Are Released
What is the role of the phage holin protein in T2 phage release?
The phage holin protein forms pores in the host cell membrane, creating a pathway for the endolysin to enter the cell.
How does the timing of phage release affect the efficiency of infection?
The timing of phage release is crucial for ensuring that the phage progeny is released before the host cell’s immune defenses can neutralize them.